March 2015, v.1.12
Current version: v.2.5
Updated: August 2016
Feedback/Comments :: View Release Notes
- Overview
- Methodology
- Background
- Biochemical Pathway and Nutrition Treatment Rationale
- Nutrition Assessment
- Comparative Standards
- Nutrition Problem Identification
- Nutrition Intervention
- Nutrition Recommendations
- 1. Nutrition intervention for appropriate nutrient intake
- 2. Nutrition intervention to achieve appropriate blood PHE concentration
- 3. Strategies for nutrition intervention
- 4. Monitoring nutrition intervention
- 5. Nutrition intervention with alternative or adjunctive therapies
- 6. Nutrition intervention before, during and after pregnancy
- Monitoring and Evaluation
- Resources
- Benefits and Harms of Implementing the Recommendations
- Barriers to Implementation
- Areas for Future Research
- List of Tables
-
Literature Evidence Summary Tables
- T.1 Laboratory and Clinical Findings in PKU
- T.2 Classification of PKU
- T.3 Recommended Intakes of PHE, TYR and Protein for PKU
- T.4 Nutrition Problem Identification for PKU
- T.5 Comparison of Recommendations for Dietary Protein Intake for Infants and Children under 4 Years of Age to the 2015 GMDI/SERC Guideline Recommendation
- T.6 Classification of Medical Foods for PKU
- T.7 Recommendations for Nutrient Intake and Sources in the Dietary Treatment of PKU
- T.8 Monitoring Nutritional Management of PKU
- T.9 Recommendations for Neurocognitive Testing in PKU
PKU Toolkit Tables- T.10 Recommended Intake of PHE, TYR, Protein and Energy for an Infant with PKU
- T.11 Composition of Breast Milk, Infant Formula, and Medical Food for an Infant with PKU
- T.12 Calculation of Formula Mixture Containing Breast Milk and Medical Food for an Infant with PKU
- T.13 Calculation of Formula Mixture Containing Infant Formula and Medical Food for an Infant with PKU
- T.14 Monitoring Nutritional Management for an Infant with PKU
- T.15 Calculation of Modified Formula Mixture Using Breast Milk for an Infant with PKU
- T.16 Current Daily Nutrient Intake for an Older Infant with PKU
- T.17 Composition of Infant Formula and Medical Food for an Older Infant with PKU
- T.18 Calculation of Daily Nutrient Intake Goals for an Older Infant with PKU
- T.19 Sample Menu Introducing Solid Food for an Older Infant with PKU
- T.20 Recommended Intake of PHE, TYR, Protein and Energy for a Child, Adolescent or Adult with PKU
- T.21 DRI Ranges for Recommended Intake of Protein and Energy for Childhood through Adulthood by Gender and Age
- T.22 Composition of Medical Food for a Child with PKU
- T.23 Calculation of Nutrient Intake Goals for a Child with PKU
- T.24 Sample Menu for a Child with PKU Eating Lunch at School
- T.25 Monitoring Nutritional Management of PKU in a Young Child
- T.26 Composition of Medical Food for a Young Adult with PKU
- T.27 Calculation of Dietary Intake for the Young Adult with PKU
- T.28 Sample Menu for a Young Adult with PKU Transitioning to Self Care
- T.29 Monitoring Nutritional Management of PKU in the Older Child, Adolescent and Adult
- T.30 Sample menu for a Young Adult with PKU Transitioning to Self Care with a Simplified Diet
- T.31 Composition of Medical Food for a Child with PKU Before Taking Sapropterin
- T.32 Calculation of Daily Nutrient Intake Goals for a Child with PKU Before Taking Sapropterin
- T.33 Baseline Blood PHE and PHE Intake for a Child with PKU Before Taking Sapropterin
- T.34 Blood PHE and Dietary PHE Intake for a Child with PKU During a Trial of Sapropterin
- T.35 Calculation of Daily Nutrient Intake Goals for a Child with PKU While Taking Sapropterin
- T.36 Sample Menu Liberalized for a child with PKU While Taking Sapropterin
- T.37 Recommended Intakes of PHE, TYR, Protein and Energy in Pregnancy for a Woman with PKU
- T.38 Composition of Medical Food in Pregnancy for a Woman with PKU
- T.39 Calculation of Daily Nutrient Intake Goals in Early Pregnancy for a Woman with PKU
- T.40 Sample Menu for a Woman with PKU in Early Pregnancy
- T.41 Recommendations for Healthy Weight Gain During Pregnancy
- T.42 Monitoring Nutritional Management of PKU During Pregnancy and Lactation
- T.43 Sample Menu for a Woman with PKU in Late Pregnancy
- References
- Contributors
- Appendix A: Recommendation Rating Definitions
- Appendix B: Terms
- Disclaimer
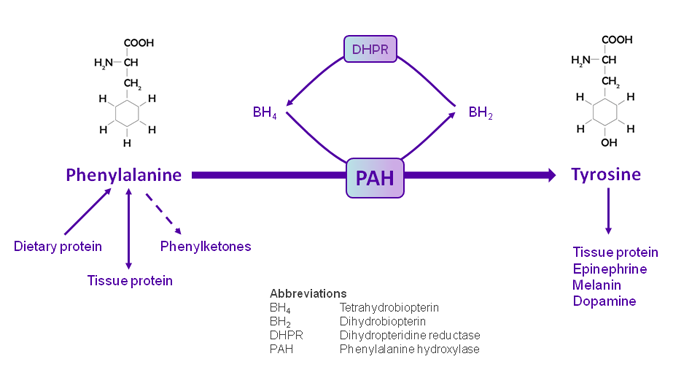
Exogenous (dietary) PHE is an essential amino acid necessary for protein synthesis and is also used as an endogenous alternative energy source during muscle protein catabolism. The initial step in PHE catabolism is an irreversible hydroxylation step to form L-TYR.
TYR, whether derived from PHE or from the diet, is used in anabolic processes (protein synthesis), as a precursor for synthesis of the neurotransmitter dopamine, and of melanin, or is catabolized for energy. In PKU, TYR becomes a conditionally essential amino acid.
Figure 2: PHE Catabolism by PAH
Goals of medical nutrition therapy in PKU are to: reduce and maintain blood PHE between 120-360 µmol/L throughout the lifespan; maintain blood TYR in the normal range; and promote normal growth, development and health maintenance.


